Isomenthol
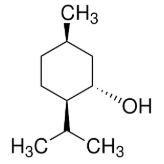
Isomenthol is a stereoisomer of menthol, a monoterpene alcohol commonly found in mint plants. It has a molecular formula of C10H20O and a molecular weight of 156.26 g/mol. Below is a detailed overview of its properties, applications, and significance:
Chemical Properties
- Structure: Isomenthol is a cyclohexanol derivative with three stereocenters, making it one of the four stereoisomers of menthol (along with menthol, neomenthol, and neoisomenthol).
- Physical Properties:
- Melting Point: 82.5°C (for the right-handed enantiomer).
- Boiling Point: Approximately 218°C.
- Density: 0.9±0.1 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and chloroform.
- Optical Rotation: +25.9° (for the right-handed enantiomer).
Applications
Isomenthol is primarily used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries due to its cooling and anti-inflammatory properties. Its applications include:
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Local Anesthetics: Used in topical creams and sprays to relieve muscle pain and arthritis.
- Respiratory Products: Helps alleviate nasal congestion and respiratory discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory Agents: Reduces skin inflammation and swelling.
- Digestive Aids: Used in treatments for gastric ulcers and gastritis.
- Cosmetics:
- Skin Care: Incorporated into products to soothe itching and irritation.
- Oral Care: Added to toothpaste and mouthwash for its refreshing flavor and antibacterial properties.
- Other Uses:
- Insect Repellents: Utilized in natural insect repellents due to its cooling effect.
- Flavoring Agent: Used in food and beverages for its minty flavor.
Synthesis
Isomenthol is typically synthesized through the catalytic hydrogenation of thymol or the cyclization of citronellal. It can also be derived from the stereoisomeric separation of menthol mixtures.
Safety and Precautions
- Toxicity: Isomenthol is generally considered safe for topical and oral use in regulated amounts. However, excessive exposure may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Regulations: Its use in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics must comply with local safety standards and guidelines.
Comparison with Menthol
While isomenthol shares many properties with menthol, its stereochemistry results in differences in odor, taste, and cooling intensity. For example, L-menthol is known for its superior cooling effect and pleasant minty aroma compared to its isomers.
Conclusion
Isomenthol is a versatile compound with significant applications in medicine, cosmetics, and flavoring. Its unique stereochemistry and properties make it a valuable alternative to menthol in various formulations. However, further research is needed to fully explore its potential and ensure its safe use.